Database
Database system: software(DBMS), hardware and users. focusing on OLTP(On-Line Transaction Processing)
Data Warehouse: Store decision-support data rather than application-oriented data, focusing on OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) eg. Amazon Redshift, Hive
Entity-Relationship (ER) Model: Entities, Properties, Relationships
3NF
1NF—all underlying fields contain atomic(scalar) values only
2NF—it is 1NF and every non-key field is irreducibly dependent on the primary key
3NF—it is 2NF and all non-key fields are mutually independent.
Concurrency
- The lost update problem (丢失修改)
- The uncommitted dependency problem (读“脏”数据问题)
- The inconsistent analysis problem (不可重复读问题)
Using lock: •Exclusive locks (X locks) / write locks 排它锁 •Shared locks (S locks) / read locks共享锁
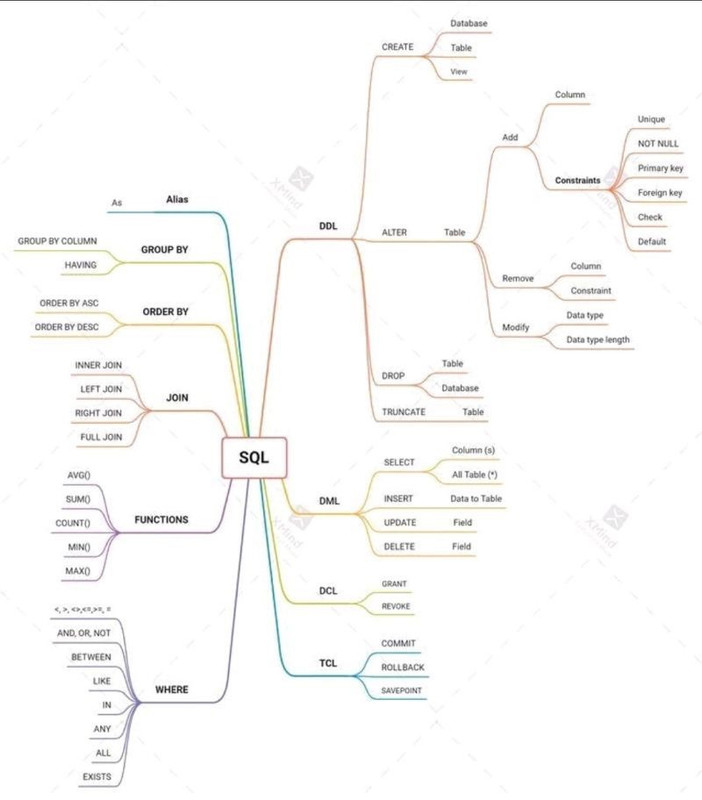
DDL DML DCL
DDL: Data Definition Languages create、drop、alter, truncate
DML: Data Manipulation Language insert、delete、udpate、select
DCL: Data Control Language grant、revoke
TCL: Transaction Control Language commit, rollback, savepoint
DELETE, DROP and TRUNCATE
| DELETE | DROP | TRUNCATE |
|---|---|---|
DELETE FROM ... WHERE... |
DROP TABLE... |
TRUNCATE TABLE ... |
| delete item, table | drop table, index, view,database | truncate table |
| just data | data and structure | just data (increase from 1) |
| DML, can rollback | DDL, can’t rollback | DDL, can’t rollback |
| slow | fastest | fast |
- delete 和 truncate 仅仅删除表数据, drop 连表数据和表结构一起删除
- delete 是 DML 语句,操作完以后如果没有不想提交事务还可以回滚,truncate 和 drop 是 DDL 语句,操作完马上生效,不能回滚
- manipulation speed: drop>truncate>delete
JOIN
difference between cross join, left join, right join, inner join, outer join
After inner join, the row number
- is more: there are some duplicate numbers in the link
- is less: there is null in the link
After left join, the row number is more than a: have duplicate numbers in the link
use group by to reduce the redundancy
Attention
A: SELECT * FROM a INNER JOIN b ON a.id = b.id
and
B: SELECT * FROM a,b WHERE a.id = b.id
Have the same result, but A may be more efficient.
Some databases do not support B, so better not to use this
especially when don’t have where for B, it’s a cross-join…
Index
create an index: CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column_list) or
alter table table_name add primary key (column)
MySQL will create a BTree index, and only scan the definite lines, which promotes the efficiency
add explain before select
delete the index:
DROP INDEX [indexName] ON [table_name];
alter table [table_name] drop index [index_name] ;
show the index: SHOW INDEXES FROM table
some types of INDEX: PRIMARY KEY, UNIQUE, FULLTEXT, INDEX
but takes more memory and is hard to maintain
View
a virtual table doesn’t contain data, just save it as a logical sentence
Pros:
- simple, don’t need to care about the structure of the table
- safe, only to the users who have the authority can visit the view
- independence, when the data change, the view doesn’t change
create the view: create view <view_name>(column_list) as select... with check option
check the information: show create view view_name
modify the view: create or replace view view_name as select...
for view, DML is limited: no distinct, no group by, no order by, no join tables…
delete the view: DROP VIEW [IF EXISTS] view_name [, view_name]
attention: 对视图进行delete、update、insert等dml操作,原表同样会更新
Add a new row or column
CREATE
database, view, table
UPDATE
UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table_name
SET
column_name1 = expr1(or select...),
column_name2 = expr2,
...
[WHERE
condition];
INSERT
insert…value and insert…set
INSERT INTO <table_name> [ <col_1>...] ]VALUES ... ]
INSERT INTO <table_name> SET <col1> = <value1>, <col2> = <value2>...
ALTER
ALTER TABLE table_name action1[,action2,…]
can change the structure of the table: add col, drop col, modify the primary key, type, rename…
add a new column: ALTER table table_name... ADD COLUMN ....after...
delete a column: ALTER TABLE tasks DROP COLUMN description
add auto_increment: ALTER TABLE ... CHANGE COLUMN col ...type... AUTO_INCREMENT;
AUTO_INCREMENT
when the increment run out: change the type int to BigInt, or separate the database
now the id is 1, 2, 3, 4
delete 4: the id is 5 next, not 4
then restart MySQL, id is 4: the increment is in the memory, not the data log
insert id 10, the next: 11
MySQL UUID and AUTO_INCREMENT
Pros:
- 表,数据库甚至服务器之间的UUID值是唯一的,它们允许您合并来自不同数据库的行或跨服务器分发数据库。
- UUID值不会公开有关数据的信息,因此在URL中使用它们更安全。
- 可以在避免往返数据库服务器的任何地方生成UUID值。例如,要将数据插入父表和子表,您必须先插入父表,获取生成的ID,然后将数据插入子表。通过使用UUID,您可以预先生成父表的主键值,并在事务中同时将行插入父表和子表。
Cons
- 存储UUID值(16字节)比整数(4字节)或甚至大整数(8字节)占用更多存储空间。
- 调试似乎更难,想象一下表达
WHERE id = 'df3b7cb7-6a95-11e7-8846-b05adad3f0ae'而不是WHERE id = 10 - 使用UUID值可能会导致性能问题,因为它们的大小和没有被排序。 use uuid_binary
Tips to enhance efficiency
authority management
create a new user: CREATE USER user_account IDENTIFIED BY password;
show the grant: SHOW GRANTS FOR user_account;
grant the authority: GRANT ...(all) ON database.* TO user_account;
revoke the authority: REVOKE ... ON database.* TO user_account;
Trigger
take effect when using DELETE、INSERT、UPDATE
The difference with Assertion: may trigger one when adding a table, which reduces the efficiency.
Trigger can change the data, but Assertion can’t
Function
Common Table Expressions CTE
with cte_name as...
dual
as a dummy table name in situations where no tables are referenced
Transaction
这种把多条语句作为一个整体进行操作,确保该事务范围内的所有操作都可以全部成功或者全部失败。如果事务失败,那么效果就和没有执行这些SQL一样,不会对数据库数据有任何改动。
ACID: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability
BEGIN;
....
COMMIT;//提交
ROLLBACK;//回滚
SAVEPOINT;//事务可以回滚到 savepoint 而不影响 savepoint 创建前的变化, 不需要放弃整个事务。
